Webready offers two types of rates you may use to manage your rental pricing.
Standard Rates
The first, and most common type, is the Standard Rate. A standard rate is an ongoing rate that describes the price of your rental over a specific date range. The purpose of the standard rate is to allow you to specify your rates into the future and not have to change them.
Dynamic Rates can be used in place of Standard Rates and are useful for automatic changes that occur based on the occupancy for your rentals. For more information on Dynamic Rates please see the following article: What is a Dynamic Rate?
The process for creating Standard Rates is easy with Webready.
Navigate to Rates to open up your rates calendar.

Using the Add Rates button select Add Standard Rate.
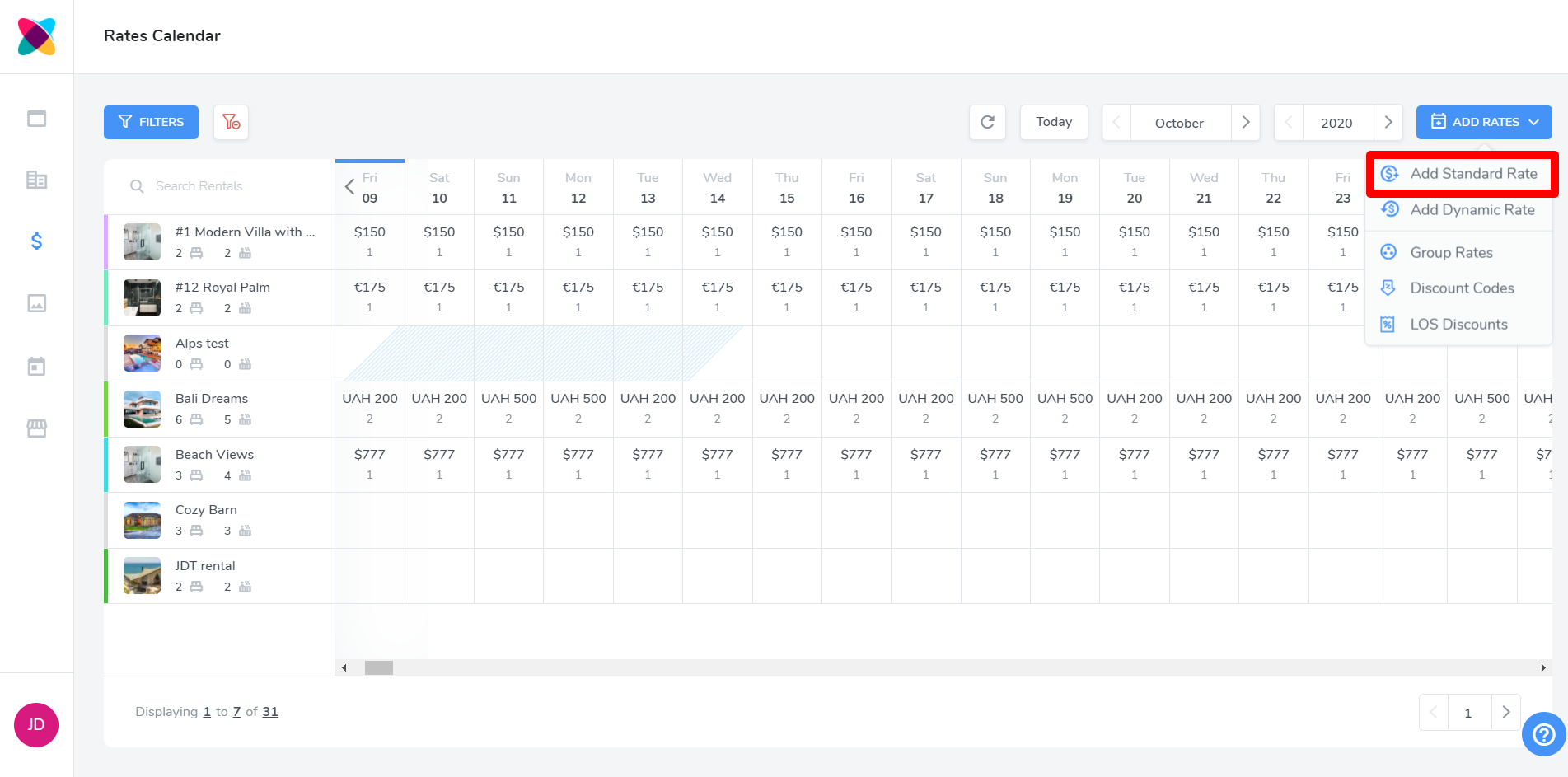
This can also be done by simply dragging on specific dates on the calendar.
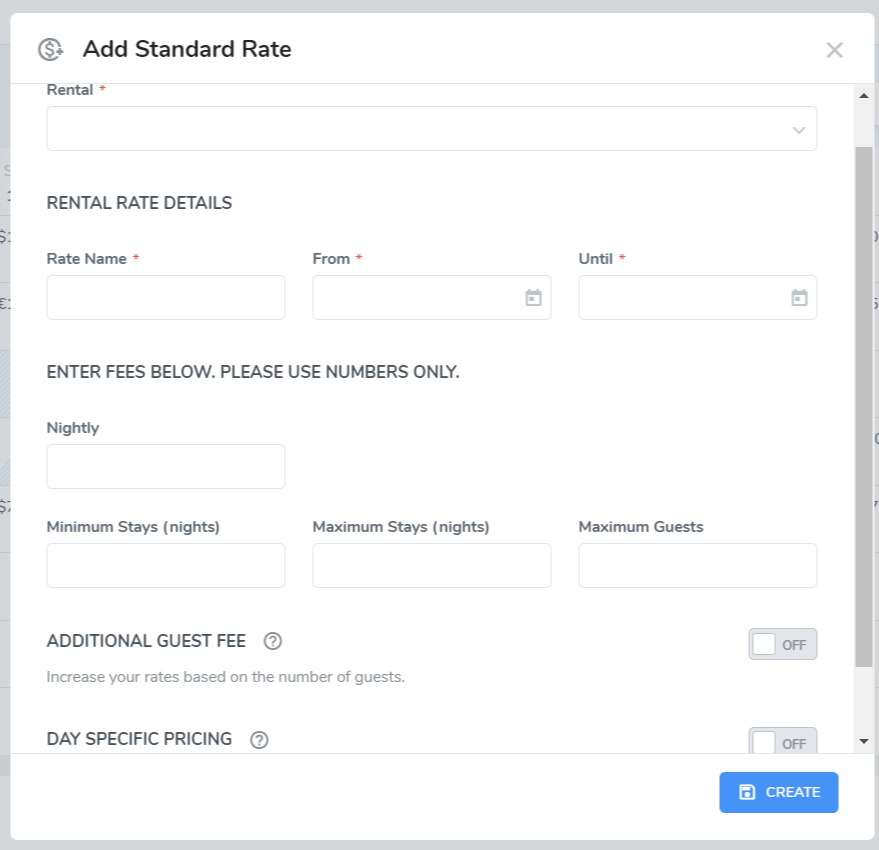
Complete required info:
Rate Name
From Date
Until Date
Nightly: nightly rate
Minimum Stay: minimum amount of days guests are allowed to book
Maximum Stay: maximum amount of days that this rental can be booked
Maximum Guests
Additional Guest Fee: charge x amount for per person per night, above y guests
Day Specific Pricing: charge a different rate for certain days of the week. Please see this Help Center article for more info.
You can create overlapping Standard rates on the Webready calendar. Webready will automatically detect the overlaps and split the existing rates appropriately to accommodate the changes.
Base Rates
The second rate type to be aware of is the Base Rate. The base rate is set on your rental rate settings and will apply to all date ranges where there is not a Standard Rate already in place. It is recommended that you use Standard Rates for creating a rate plan due to the more advanced settings mentioned in the section above. For more information on how to set a Base Rate, please see the following article: What is a Base Rate?